TSS EXCLUSIVE: New Oumuamua Origin Theory Suggests More Interstellar Visitors Will Fly By Earth In The Future
by Rhodilee Jean Dolor
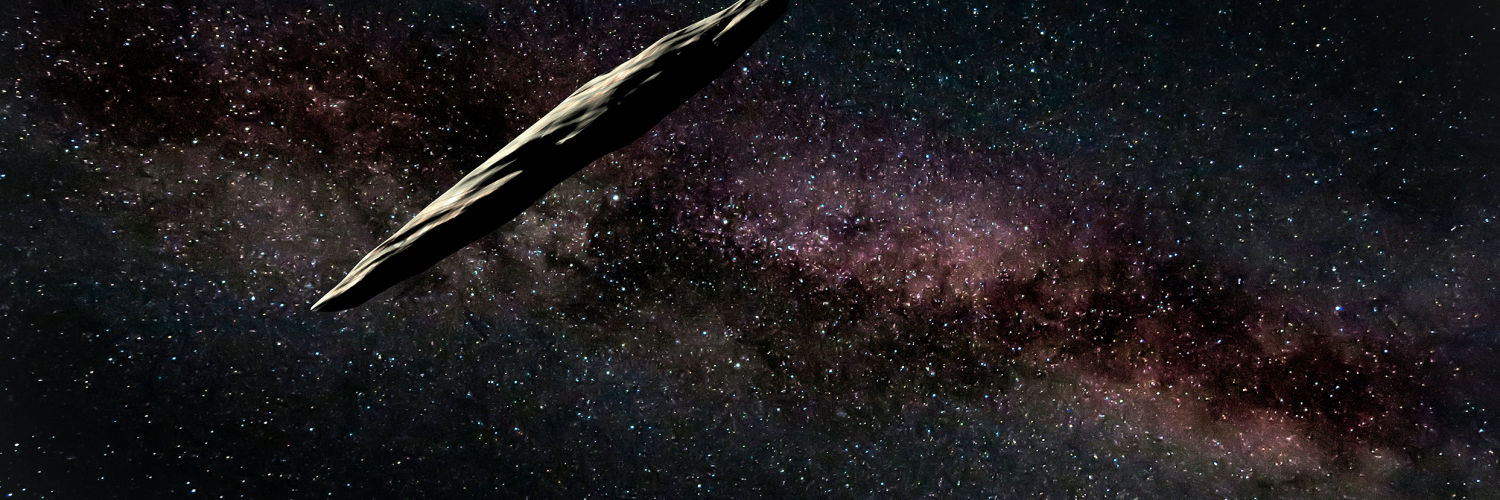
In 2017, Canadian astronomer Robert Weryk discovered a strange object from another star system passing by. The elongated, cigar-shaped body is the first of its kind that scientists found, but findings of new research on its origin and formation suggest we will see more interstellar visitors in the future.
2017年,加拿大天文学家罗伯特·韦里克(Robert Weryk)在经过地球的一个恒星系统中发现了一个奇怪的物体。这个细长的雪茄状星体是科学家们发现的第一个此类星体,但有关其起源和形成的新研究结果表明,未来我们将看到更多这样的星际游客。
Messenger From Afar
远方的信使
Researchers called the object Oumuamua, which means “a messenger from afar arriving first” in Hawaiian language. Nearly three years after it was detected using the Haleakala Observatory’s Pan-STARRS telescope in Hawaii, the body is still shrouded in mystery.
研究人员把这个物体称为“Oumuamua”,在夏威夷语中,意思是“从远方来的信使最先到达”。在夏威夷哈雷卡拉天文台的泛星望远镜探测到这个星体将近三年后,它仍然笼罩在神秘之中。
Data is scant because scientists only had two weeks to study it before it became too faint for observation as it hurtled away from Earth.
科学家只有两个星期的时间来研究它,而且它在离开地球时变得太微弱而无法观测,因此获得的有关数据不足。
New research published in the journal Nature Astronomy on April 13 offers hope that astronomers will get more opportunities to study interstellar objects like Oumuamua, and possibly settle unanswered questions about these bodies.
4月13日发表在《自然天文学》杂志上的最新研究给天文学家们带来了希望:天文学家们将有更多的机会来研究像Oumuamua这样的星际天体,并可能解决有关这些天体的尚未解答的问题。
Study researcher Yun Zhang, from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and colleagues used computer simulations to investigate how the body was formed in a bid to understand Oumuamua’s odd features that ensued a debate on whether the object is a comet or an asteroid.
来自中国科学院国家天文观测站的研究人员张云和他的同事们利用计算机模拟来研究这个天体是如何形成的,以期了解“Oumuamua”的奇怪特征,这引发了一场关于该天体是彗星还是小行星的争论。
The findings suggest that the object could be one of the remnants of a larger body that was ripped apart by its host star during tidal fragmentation.
研究结果表明,这个天体可能是一个较大天体的残余物之一,它在潮汐破碎过程中被其主星撕裂。
Tidal Fragmentation
潮汐力撕裂
The process happens when a smaller object ventures very close to a bigger one. The tidal forces of the larger body can tear the smaller body apart, just like what happened to the comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 when it got too close to Jupiter.
潮汐力撕裂通常在一个较小的物体与一个较大的物体非常接近时发生。较大天体的潮汐力会将较小的天体撕裂,就像Shoemaker Levy 9号彗星离木星太近时发生的事情一样。
The comet was once a single body but it was torn apart when it made a close approach to Jupiter in July 1992. When it was discovered in 1993, Shoemaker-Levy 9 was already torn into more than 20 pieces that orbit the planet. NASA explained that the tidal forces from Jupiter’s powerful gravity is to blame for the fragmentation of the object.
这颗彗星曾经是一个单一的天体,但在1992年7月接近木星时,它被撕裂了。到1993年被发现时,它已经被撕成20多块并环绕地球运行。美国航天局解释说,木星强大的引力所产生的潮汐力是造成该物体碎裂的原因。
The same thing may happened to Oumuamua’s parent body. It was possibly a planetesimal body, long-period comet, or an Earth-like planet that ventured too close to the parent star. Computer simulations suggest that close encounters within 186,411 miles of the star can rip objects into elongated fragments that are then ejected into interstellar space.
同样的事情也可能发生在Oumuamua的母星身上。它可能是一颗小行星,一颗长周期彗星,或者是一颗离母星太近的类地行星。计算机模拟表明,在距离恒星186411英里范围内的近距离接触会将物体撕裂成细长的碎片,然后被喷射到星际空间。
Thermal modeling also revealed that the surface of the fragments that broke away from the parent body melted at a short distance from the host star due to extreme heat, but it recondensed when the objects moved further away, causing the fragments to develop a surface crust that supports and maintains an elongated shape.
热力学模拟还显示,脱离母体的碎片表面由于极热而在距离主星很短的距离内融化,但当物体进一步远离时,它又重新聚集,导致碎片形成表面地壳,支撑并保持细长的形状。
“Oumuamua-like ISOs can be prolifically produced through extensive tidal fragmentation and ejected during close encounters of their volatile-rich parent bodies with their host stars,” the researchers wrote in their study. “Material strength enhanced by the intensive heating during periastron passages enables the emergence of extremely elongated triaxial ISOs with shape c∕a ≲ 1∕10, sizes a ≈ 100 m and rocky surfaces.”
研究人员在他们的研究报告中写道:“通过广泛的潮汐碎片化,类似Oumuamua的ISO可以大量产生,并在其挥发性母体与宿主恒星近距离接触时被喷射出去”。“在环绕宇宙轨道期间,强烈的加热而增强了材料的强度,因此出现了形状为c∕a≲ 1∕10、尺寸为a≈100 m的极长三轴等值线和岩石表面。”
The researchers added that the tidal fragmentation scenario can also explain the other odd features of Oumuamua. The object has no comet-like coma and exhibited non-gravitational acceleration during its passage. Scientists think this is not caused by the forces of planetary bodies, but by outgassing that pushes the object like thrusters that propel spacecraft.
研究人员补充说,潮汐破碎的情况也可以解释Oumuamua的其他奇怪特征。这个物体没有彗星般的彗差,在其通过过程中表现出非重力加速度。科学家们认为这不是由行星体的力量造成的,而是由气体的释放推动物体,就像推动宇宙飞船的推进器一样。
Most of the volatile substances on the object’s surface were lost as a result of heating by the star, but some residual water ice is believed to have been preserved below the surface.
由于恒星的加热,物体表面的大部分挥发性物质都消失了,但据信一些残留的水冰被保存在地表以下。
“Heat diffusion during the stellar tidal disruption process also consumes large amounts of volatiles, which not only explains Oumuamua’s surface colors and the absence of visible coma, but also elucidates the inferred dryness of the interstellar population,” Zhang said.
“恒星潮汐破裂过程中的热扩散也消耗了大量的挥发物,这不仅解释了Oumuamua的表面颜色和没有可见彗星像差的现象,而且也解释了推断出的星际种群的干燥程度。”
When Oumuamua arrived in the Solar System, additional heat from the sun seeped through the object’s crust and liberated the residual ice. The evaporating materials then gave the body the push that can explain its unusual acceleration.
当Oumuamua到达太阳系时,来自太阳的额外热量渗入了星体的外壳,释放了残余的冰。蒸发的物质给了它推力,这可以解释它的异常加速。
Common Scenario
常见场景
If the tidal fragmentation theory turns out correct, Oumuamua is just one of many other objects ejected from their star system into space. Given the number of stars in our galaxy, researchers think there are many other similar objects that were shredded from their parent bodies and ejected from their home system. “
如果潮汐力撕裂理论被证明是正确的,那么“瓦穆瓦”只是从其恒星系统喷射到太空中的许多其他物体之一。考虑到我们银河系中恒星的数量,研究人员认为还有许多其他类似的物体是从它们的母体上碎裂并从它们的主系统中喷射出来的。“
“The discovery of Oumuamua implies that the population of rocky interstellar objects is much larger than we previously thought,” Zhang said. “On average, each planetary system should eject in total about a hundred trillion objects like Oumuamua. We need to construct a very common scenario to produce this kind of object.”
“Oumuaua的发现意味着星际岩石天体的数量比我们之前想象的要大得多,”张晓东说。“平均来说,每个行星系统总共应该喷出大约100万亿个像Oumuaua这样的星体。我们需要构建一个非常常见的能生成这种东西的场景。”
More Interstellar Visitors To Pass By Earth’s Galactic Neighborhood
更多的星际游客会经过银河系乃至地球附近
The researchers also think that a number of these Oumuamua-like bodies will stray in Earth’s galactic neighborhood.
研究人员还认为,在地球的银河系附近,会有一些类似Oumuamua的天体出没。
“Oumuamua is just the tip of the iceberg. We anticipate many more interstellar visitors with similar traits will be discovered by future observation with the forthcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory,” said study researcher Douglas N. C. Lin, from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
“Oumuamua只是冰山一角。加州大学圣克鲁兹分校的研究人员道格拉斯·N·C·林说:“我们预计,在即将到来的维拉·C·鲁宾天文台的未来观测中将发现更多具有类似特征的星际游客。”。
It did not take long after the discovery of “Oumuamua that astronomers detected 2I/Borisov in August 2019. Researchers said the second interstellar object found flying by the Solar System is a comet that originated from a red dwarf, a star smaller and fainter than the sun.
“Oumuamua”发现后不久,天文学家于2019年8月探测到2I/Borisov。研究人员说,在太阳系发现的第二个星际物体是一颗彗星,它起源于一颗红矮星,一颗比太阳更小、更暗的恒星。
Based on observations using the National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers said the object is likely a fragment of a planet with lots of carbon monoxide near the surface.
天文学家说,根据使用国家射电天文观测台的Atacama大毫米/亚毫米阵列(ALMA)的观测结果,这个物体很可能是一颗行星的碎片,其表面附近有大量的一氧化碳。
“If that object collided with another, then the carbon monoxide-rich fragments could be released into space,” said Martin Cordiner, from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “After a cold, lonely voyage, 2I/Borisov made its close encounter with our Solar System and started outgassing and showing us what it’s got inside.”
“如果这个物体与另一个物体相撞,那么富含一氧化碳的碎片可能会被释放到太空中,”马里兰州格林贝尔特市美国宇航局戈达德太空飞行中心的马丁·科迪纳说。“在经历了一次寒冷而孤独的航行后,2I/Borisov与我们的太阳系进行了近距离接触,并开始释放气体,向我们展示了它的内部结构。”
Astronomers have so far detected only two interstellar visitors, but if the new theory holds up, new telescopes and instruments will eventually discover more of these objects in the future. When that happens, scientists get better opportunities to learn more about the universe and our very own Solar System.
到目前为止,天文学家只探测到两个星际访客,但如果新理论成立,新的望远镜和仪器最终将在未来发现更多这样的天体。当这种情况发生时,科学家就有更好的机会了解宇宙和我们自己的太阳系。
翻译:STARSET Mirror翻译组